The agricultural industry plays a key role in sustainability transformation. Improvements directly impact biodiversity, water quality and efficiency, soil quality, use of chemicals or carbon stocks. Sustainability labels aim to define the various measurable sustainability criteria and do compliance audits. But without knowing all field locations and documenting the field history compliance checks remain largely incomplete. Fraud can go undetected and trust in a label will suffer. Our satellite based crop mapping and monitoring forms now a reliable basis for detecting and measuring such criteria at large scale. Our automated services comprise:
- Efficiently mapping large number of fields
- Check their location in relation to protected areas like key biodiversity areas
- Check sustainability KPIs like crop rotation, cropping intensity or water use
But we also help to implement these measures at farm level by supporting farm advisory services through:
- Monitoring crop status & performance
- Assessing yields (custom)
- Determining pest and disease risks for certain crops
- Assessing water use efficiency (upcoming)
Important: On Nov 22nd 2022 EFRAG released the European Sustainability Reporting Standard (ESRS) draft. ESRS specifies the environmental, social, and governance (ESG) rules for financial reporting. Its environmental ruleset e.g. requires the identification and reporting of sites in or near biodiversity-sensitive areas, among others. The reporting company is obliged to „disclose the number and area (in hectares) of sites owned, leased or managed in or near these protected areas or key biodiversity areas“.
Key Biodiversity Areas (KBA) and other protected areas
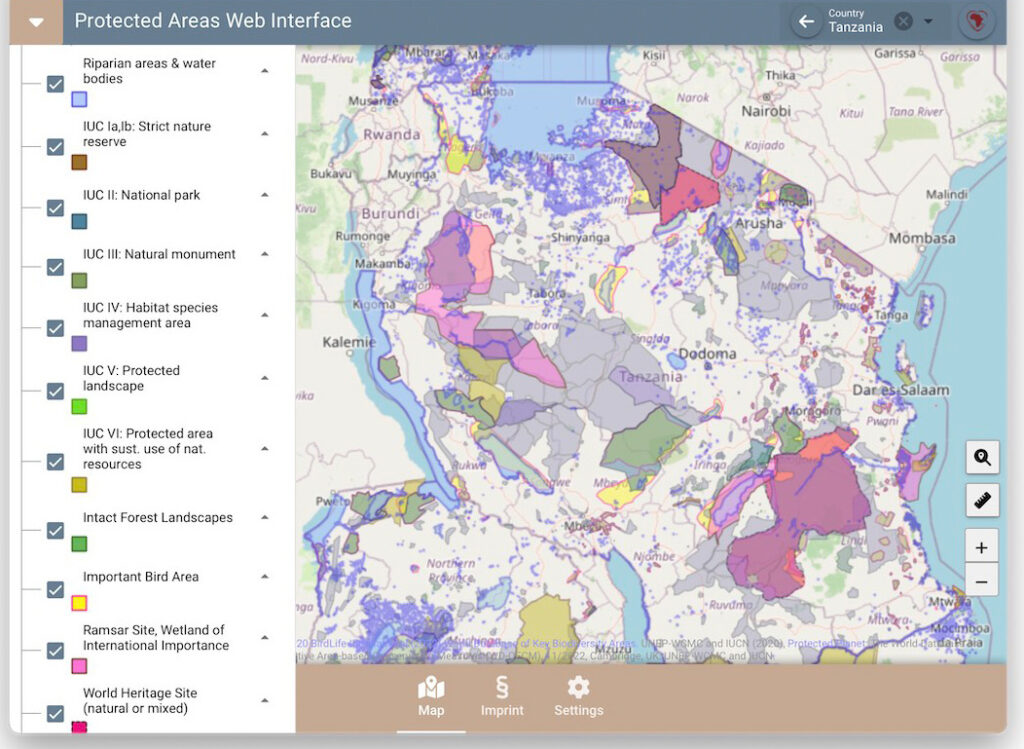
We are checking all field locations against Key Biodiversity Areas and other protected areas as required by the ESRS guidelines. As basis we are using the World Protected Areas Dataset (WDPA). Our services include the identification of all field locations through an efficient crop mapping process. In particular when field locations change annually due to crop rotation like cotton. But also for permanent crops like cocoa or coffee.
Sustainability KPI
We are checking remotely different good agricultural practices (GAP) at field level such as:
- Crop rotation
- Winter cover
- Crop cover ratio
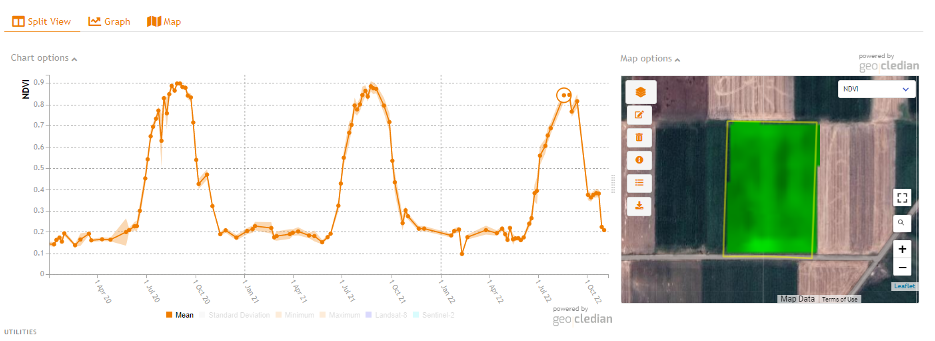
Above a cotton without crop rotation for three consecutive years.
References

For CmiA we compiled the protected areas of 10 African countries. These are provided through a web-viewer to auditors and cotton companies. The data set is used for checking the protected areas and biodiversity compliance. CmiA is a sustainability standard for Aid by Trade Foundation.
